Wall Street Journal
From Gitmo to Miranda, With Love
How the American left feted and freed a Guantanamo inmate who then killed in Iraq.
By Debra Burlingame, July 30, 2008 (with additional links added here)
Captive Miranda, Lord knows I have not given a thought to the paperwork you sent me. Let me tell you, Captive, that our release is not in the hands of the lawyers or the hands of America. Our release is in the hands of He who created us.
The poem, “To My Captive Lawyer, Miranda,” was written by Abdullah Saleh Al-Ajmi while he was a detainee at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba. No doubt, it would have given the former detainee, who was released in 2005, immense satisfaction to know that his last earthly deed was referenced in Justice Antonin Scalia’s dissenting opinion in Boumediene v. Bush. That’s the recent Supreme Court decision that gave Guantanamo detainees the constitutional right to challenge, in habeas corpus proceedings, whether they were properly classified by the military as enemy combatants.
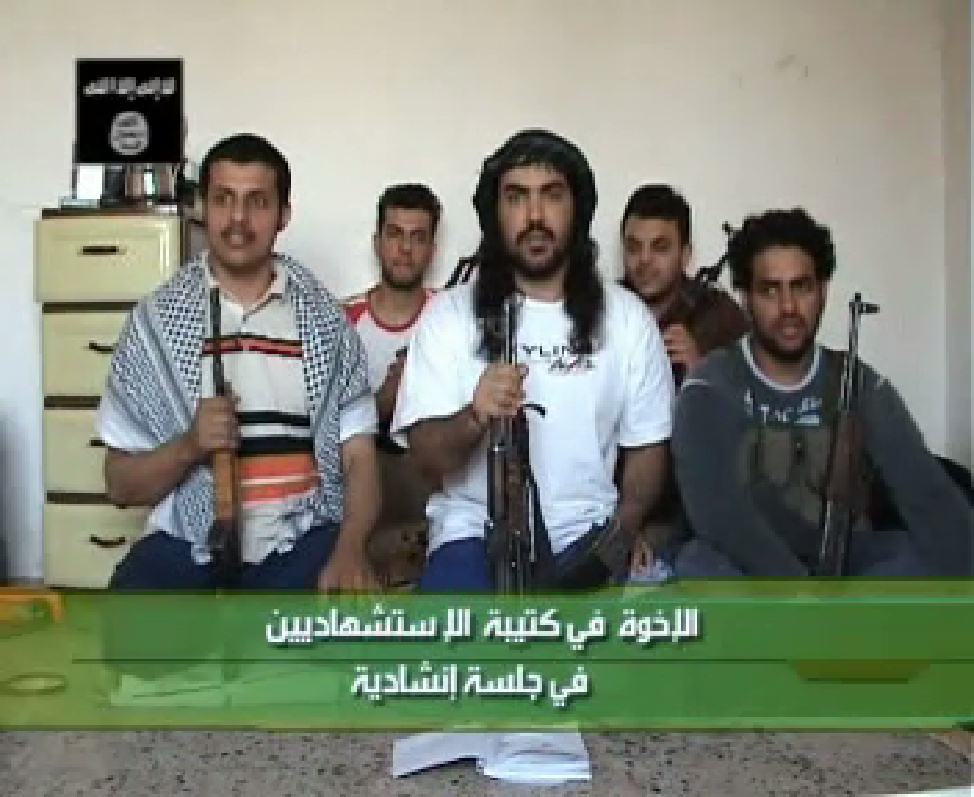
Abdullah Saleh Al-Ajmi, on the left, in a martyrdom video posted on an al Qaeda Web site.
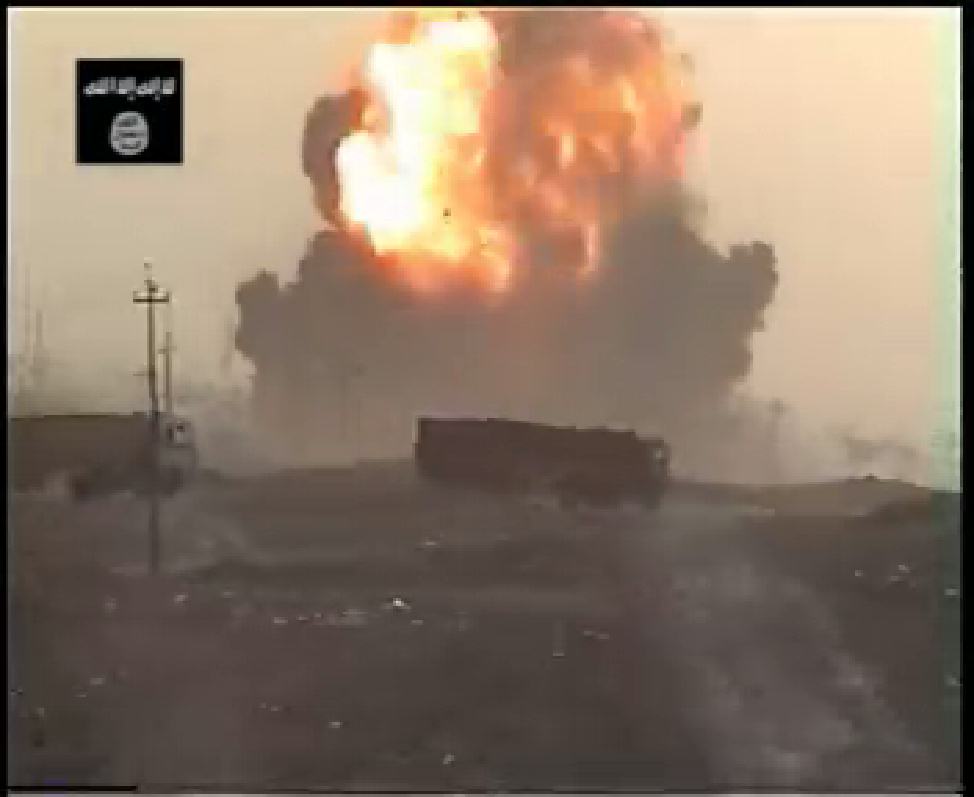
Al-Ajmi, a 29-year-old Kuwaiti, blew himself up in one of several coordinated suicide attacks on Iraqi security forces in Mosul this year. Originally reported to have participated in an April attack that killed six Iraqi policemen, a recent martyrdom video published on a password-protected al Qaeda Web site indicates that Al-Ajmi carried out the March 23 attack on an Iraqi army compound in Mosul. In that attack, an armored truck loaded with an estimated 5,000 to 10,000 pounds of explosives rammed through a fortified gate, overturned vehicles in its path and exploded in the center of the compound. The huge blast ripped the façade off three apartment buildings being used as barracks, killing 13 soldiers from the 2nd Iraqi Army division and seriously wounding 42 others.
Using the name “Abu Juheiman al-Kuwaiti,” Al-Ajmi is seen on the video brandishing an automatic rifle, singing militant songs and exhorting his fellow Muslims to pledge their allegiance to the “Commander of the Faithful” in Iraq. Later, Al-Ajmi’s face is superimposed over the army compound, followed by footage of the massive explosion and still shots of several dead bodies lying next to the 25-foot crater left by the blast.
Bill Roggio / The Long War Journal — Abdullah Saleh Al-Ajmi killed 13 people in this March 23 truck bombing in Mosul, Iraq—after he was released from U.S. custody at Guantanamo Bay.
Screen shot from martyrdom video posted on an al Qaeda web site of Abdullah Saleh Al-Ajmi detonating his truck bomb, killing himself and 13 of his fellow Muslims in Mosul on March 23, 2008.
In 2006, Al-Ajmi’s “Miranda” poem was included in a recitation of detainee poetry at a “Guantanamo teach-in” sponsored by Seton Hall Law School. The all-day event was Webcast live to 400 colleges and law schools across the country and abroad. Some of the lead attorneys pushing for detainee rights participated in the event, which began with organizers boasting about the diversity of the event’s participating schools as exemplified by the American University of Paris, the American University in Cairo, the U.N. University for Peace in Costa Rica, Princeton Theological Seminary, and Parsons School of Design in New York City. One of Al-Ajmi’s lawyers gave a presentation about detainee treatment entitled, “Insults to Religion.”
Marc Falkoff, a former Covington & Burling attorney-turned-law-professor who represents several detainees, read the poems and later published a selection of them in a book (“Poems from Guantanamo: The Detainees Speak,” Iowa University Press, 2007.) In his introductory remarks to the students, Mr. Falkoff described Al-Ajmi and the other detainee poets as “gentle, thoughtful young men” who, though frustrated and disillusioned, expressed an abiding hope in the future. “One thing you won’t hear is hatred,” he said, “and the reason you won’t hear it is not because I edited it out, it’s because it’s not there in the poetry.” Then how to explain the fact that — on the advice of Al-Ajmi’s attorneys — “To My Captive Lawyer, Miranda,” was excluded from the published collection last year? Mr. Falkoff, who also has a Ph.D. in literature, refused to explain further, though he insists on describing Al-Ajmi’s verse as a “love poem to his lawyer.”
Miranda, antelope, I am madly in love with captive Roman gazelles. I pledge that if I ever see you outside this jail, I shall capture you and take you in a starry night.
In light of Al-Ajmi’s deadly suicide attack, his poem seems less, as Mr. Falkoff insisted in a recent interview, “a trope about being a prisoner of love,” and more about taunting his lawyers and mocking the American legal system. As any devotee of the successful “Law & Order” television franchise knows, “Miranda” is more than a fanciful female name. It is also the name of another infamous prisoner — Ernesto Miranda, the career criminal and itinerant sex offender whose 1966 landmark legal case resulted in the “Miranda rule,” requiring law enforcement officers to inform criminal suspects in custody of their right to remain silent and their right to an attorney during questioning.
It is easy to imagine the detainees’ attorneys, upon first arriving at Guantanamo in 2004, earnestly explaining to their incredulous clients how the Miranda warning works. Incredulous, because detainees would certainly grasp that extending the full array of Fifth and Sixth Amendment rights to unlawful enemy combatants would have a devastating effect on vital intelligence-gathering efforts. Indeed, lawyers have already become part of the al Qaeda tool kit. When Khalid Sheikh Mohammed was apprehended in Pakistan in 2003 and handed over to the U.S., he reportedly told his initial interrogators, “I’ll talk to you guys when you take me to New York and I can see my lawyer.”
After the Boumediene decision, that is no longer an empty threat. While Justice Anthony Kennedy stated in his 5-4 majority opinion that detainees are entitled to habeas review in the federal courts, he failed to expressly outline what legal standards the government would have to meet for detainee cases to pass constitutional muster. Many legal experts contend that if the habeas lawyers succeed in attaining for detainees the same degree of procedural rights as those extended to ordinary criminal defendants in domestic cases, “lawyering up” would mean the end of terrorist questioning, not the beginning.
If this is what “Miranda” represents, no wonder an Islamist suicide bomber would love her.
Miranda, what can I say? The heart is incarcerated in prisons of injustice, tortured and deprived, targeted with sharp, poisoned arrows by the hands of oppressors who have no mercy. Tell the mothers about their sons, the prisoners, brothers in bondage … they shall walk home.
But many in the detainees’ home countries aren’t welcoming them with open arms. The bombings carried out by Al-Ajmi and two other Kuwaiti nationals have stirred a public outcry from their fellow citizens. Al-Ajmi’s own father has reportedly threatened to sue the government of Kuwait for issuing his son a passport and failing to live up to the terms set forth in the transfer agreement with U.S. State Department as a condition of his release. Kuwait’s negligence and the State Department’s failure to follow up have resulted in calls from the public for the detainees to stay right where they are and for Guantanamo to stay in operation.
“I believe the U.S. State Department knows the prisoners well, their way of thinking, and their plans after being released from prison,” wrote Ali Ahmad Al-Baghli, Kuwait’s former Minister of Oil, in the Arab Times after news of Al-Ajmi’s suicide attack broke. He specifically criticized the outspoken leader of the Kuwaiti detainee families committee, Khalid Al-Odah, (interestingly, he is one of the “translators” Mr. Falkoff acknowledges in his poetry book), whose son remains at Guantanamo. Al-Odah hired a Washington, D.C., public-relations firm to “humanize” the detainees with sympathetic press.
“We cannot romanticize them into fallen heroes of Western neo-imperialism,” wrote Shamael Al-Sharikh, a columnist for the Kuwaiti Times, in an article advocating that Guantanamo stay open, “because we are as much potential victims of terrorist attacks as [Americans] are.”
As an example of where we might be headed after Boumediene, consider the situation in Britain. In June, Abu Qatada, a radical imam wanted in connection with bombing conspiracies in several countries, was released from jail after seven years of fighting his deportation. Qatada, whose recorded sermons were found in the Hamburg apartment of the 9/11 hijackers, was described by an immigration appeals commission as a “truly dangerous individual” who was “heavily involved, indeed at the center of terrorist activities associated with al-Qa’eda.”
But judges in Britain will not extradite him to Jordan, where he was convicted in absentia, because his lawyers allege that the evidence against him might have been obtained by torture. Sending him packing under these circumstances, the court ruled, would violate the European Convention on Human Rights.
The result is a perverse situation in which, to protect the human rights of the man who issued a fatwa to kill the wives and children of Egyptian police and army officers, the British public pays a yearly tab of $1.1 million to cover Qatada’s round-the-clock police surveillance, housing and welfare assistance for him, his wife and five children.
For those who scoff at the idea that U.S. judges would release a dangerous terrorist here, think again. As Attorney General Michael Mukasey pointed out in a speech earlier this month at the American Enterprise Institute, the Boumediene decision was vague on every detail but one. The ruling said that for habeas review to mean anything, the court must have the power to release. What do we do with a graduate of al Qaeda training camps who hasn’t yet committed an act of violence? What do we do if no country will take him? If Congress doesn’t intervene, the most difficult detainee cases may end up being administered by federal judges who are dismissive of concerns about enemy combatants returning to the battlefield.
“Courts guarantee an independent process, not an outcome,” wrote John Coughenour, the federal judge who presided over the trial of “millennium bomber” Ahmad Ressam in a Washington Post op-ed just this Sunday. Yes, and that is precisely why Congress has an obligation to formulate the substance and parameters of that process. Judges do not make law or policy. The scope of their review is limited to the immediate case before them.
Unless Congress weighs in, judges — unaccountable to the body politic — will decide what standards of proof and rules of evidence will apply to these detainees, resulting in an ad hoc, case-by-case body of law which focuses on the rights of the detainees, not on the consequences for our war fighters who risk their lives to capture them. Since when do we leave it to judges to decide when and to what degree our troops are required to engage in police duties in the heat of battle?
Further, judges only rule on the applications made by the lawyers who come before them. Despite their rhetoric about “rule of law,” attorneys are not charged with acting in furtherance of the national security interests of the public. Their obligation is to their clients alone, the detainees. Hence, we have witnessed the six-year campaign by Gitmo lawyers to pressure the U.S. government into releasing dangerous men before their cases come before a military tribunal or are heard in the federal courts.
David Cynamon, a senior attorney at Pillsbury Winthrop Putnam Shaw, is one of the lead lawyers negotiating the repatriation of the Kuwaiti detainees. In an email last fall to Pentagon officials, Mr. Cynamon expressed frustration with what he perceived as foot-dragging in the release of the last four Kuwaitis still held at Gitmo. He attached an exhibit which compared the unclassified information on all original 12 Kuwaiti detainees who were captured in Afghanistan. “I find it impossible to deduce from this chart,” he wrote, “that the four who remain are any more (or less) [sic] dangerous than the ones who were returned.” After Al-Ajmi’s devastating suicide attack in Mosul, one hopes the Pentagon is giving his chart a second look.
Meanwhile, the habeas attorneys’ effort to smear the United States and paint their clients as innocent victims continues. “Poems from Guantanamo” was taught this spring in an undergraduate course called “Writers in Exile” at City University of New York in Queens, a short distance from Ground Zero. The book’s introduction states that the detainee poets “follow in the footsteps of prisoners who wrote in the Gulag, the Nazi concentration camps, and, closer to home, Japanese-American internment camps.” One of the students, posting on the class blog, wrote of the detainees’ plight, “Wow, I had no idea. For the first time in my life, I am ashamed to be seen as an American.”
Your whole being and your heart will be captivated by this night, who drove the Romans to madness. You will forget everything about Rome and will live the life of faith in Islam.
Abdullah Salem Al-Ajmi, the detainee who wrote of turning the tables on his lawyer, Miranda, should haunt the dreams of every member of Congress.
——
Editor — Ms. Burlingame, a former attorney and a director of the National September 11 Memorial Foundation, is the sister of Charles F. “Chic” Burlingame III, the pilot of American Airlines flight 77, which was crashed into the Pentagon on Sept. 11, 2001. In addition, she co-founded 9/11 Families for a Safe & Strong America, in 2004.